Tularemia Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
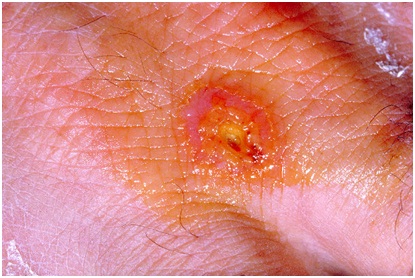
What Is Tularemia?
Tularemia, also called rabbit fever or deer fly fever, is a rare infectious disease that typically attacks the skin, eyes, lymph nodes and lungs.
It is caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis.
The bacteria are passed to humans through contact with tissue from the infected animal. It can also be passed via ticks, biting flies, and mosquitoes.
Different types of tularemia include:
- Ulceroglandular tularemia
- Glandular tularemia
- Oculoglandular tularemia
- Oropharyngeal tularemia
- Pneumonic tularemia
- Typhoidal tularemia
Causes Of Tularemia:
Tularemia doesn’t naturally occur in humans and isn’t known to be contagious.
It is known to occur due to exposure of mammals infected by Francisella tularensis.
Tularemia has several modes of transmission, which include:
- Insect bites
- Ticks
- Deer flies
- Exposure to sick or dead animals.
- Airborne bacteria.
- Contaminated food or water
Symptoms Of Tularemia:
Some common symptoms, exhibited in all types of tularemia, include:
- Chills
- Eye irritation (conjunctivitis, if the infection began in the eye)
- Fever
- Headache
- Joint stiffness
- Muscle pains
- Red spot on the skin, growing to become a sore (ulcer)
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Weight loss
Other symptoms vary depending upon the type of tularemia.
- Ulceroglandular tularemia
- A skin ulcer that forms at the site of infection — usually an insect or animal bite
- Swollen and painful lymph glands
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Exhaustion
- Oculoglandular tularemia
- Eye pain
- Eye redness
- Eye swelling and discharge
- An ulcer on the inside of the eyelid
- Sensitivity to light
- Oropharyngeal tularemia
- Fever
- Throat pain
- Mouth ulcers
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Inflamed tonsils
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Pneumonic tularemia
- Dry cough
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Typhoidal tularemia
- High fever
- Extreme exhaustion
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Enlarged spleen
- Enlarged liver
- Pneumonia
Diagnosis Of Tularemia:
The following tests are performed in order to diagnose tularemia:
- Blood culture for the bacteria
- Blood test measuring the body’s immune response to the infection (serology for tularemia)
- Chest x-ray
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test of a sample from an ulcer
Treatment Of Tularemia:
Tularemia is generally treated via medications which include:
- Streptomycin
- Gentamicin
- Oral antibiotics
- doxycycline
- Oracea,
- Vibramycin,
Related Articles:
Swimmers Itch Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cold Sores Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Hemangioma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Progeria Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Raynaud’s Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Stye Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Castleman Disease Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
Diaper Rash Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cellulitis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Tinea Versicolor Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Prickly Heat Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
By : Natural Health News




