Cystic Fibrosis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Cystic Fibrosis?
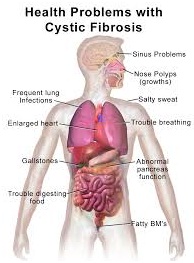
A genetic disorder, cystic fibrosis tends to majorly affect lungs while also affecting the pancreas, liver, kidneys and intestine.
It is a life threatening disease as the persistent ling infection may make it difficult for the affected individual to breath.
Inherited in an autosomal manner, it is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies of the gene for a protein. Having a single copy of the mutated gene leads an individual to become a carrier.
This protein is responsible for producing mucus, sweat and digestive juices. Having cystic fibrosis leads to these fluids to become thick and sticky thereby causing problems.
Although cystic fibrosis cannot be cured, antibiotic treatment may help in managing lung infections.
Approximately one out of every 3000 newborns is affected by cystic fibrosis and about one in 25 people are carriers.
Causes Of Cystic Fibrosis:
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a genetic mutation in the gene called cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR).
There are over 1500 types of mutations which bring about cystic fibrosis. However, the most common one is ΔF508 (deletion of three nucleotides).
The CFTR gene is responsible for production of fluids ranging from mucous to digestive juices. When mutation occurs, CFTR tends to produce thick, sticky fluids.
In order to develop the disease, a child must inherit a copy of the mutated gene from both his mother and father. In case of having one copy, the child will be a carrier and would not develop cystic fibrosis.
Symptoms Of Cystic Fibrosis:
The following signs and symptoms are exhibited:
- Very salty-tasting skin
- Persistent coughing, at times with phlegm
- Frequent lung infections including pneumonia or bronchitis
- Wheezing
- Poor growth or weight gain in spite of a good appetite
- Male infertility
- Breathlessness
- Exercise intolerance
- Inflamed nasal passages or a stuffy nose
- Foul-smelling, greasy stools
- Intestinal blockage, particularly in newborns
- Severe constipation
Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis:
The following tests are conducted in order to diagnose cystic fibrosis:
- Blood sample taken to detect higher than normal levels of a chemical (immunoreactive trypsinogen) released by the pancreas.
- Sweat test, to see if sweat is saltier than normal.
- Genetic testing, to check for specific defects on the gene responsible for cystic fibrosis.
Treatment Of Cystic Fibrosis:
While there is no cure for cystic fibrosis, it can be managed via treatment. The following treatment options are available:
- Medications
- Chest physical therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Lung transplant
- Bowel surgery
- Feeding tube
- Endoscopy
- Nasal polyp removal
By : Natural Health News




