Skin Health – Granuloma Annulare, Acne, Sun Protection, Anti-aging

Maintaining optimal skin health is more than just a cosmetic priority—it’s a reflection of our internal well-being. The skin is our largest organ and serves as a protective barrier against environmental aggressors like bacteria, UV radiation, and pollutants. Over the years, researchers have emphasized the importance of nurturing our skin to prevent and manage conditions such as granuloma annulare, acne, and signs of aging, while also highlighting the necessity of sun protection. How to care for your skin, prevent common skin disorders, and achieve long-term skin vitality.
Understanding Skin Health
Skin health refers to the skin’s overall condition—its texture, hydration, resilience, and ability to perform essential functions like temperature regulation, immune defense, and sensation. A healthy skin barrier is smooth, evenly colored, and resilient to injury or irritation.

However, several factors can compromise skin health, including:
- Genetics
- Hormonal imbalances
- Environmental stressors
- Aging
- Poor nutrition
- Chronic illnesses
Addressing these factors holistically is key to preventing skin problems and achieving radiant, youthful skin.
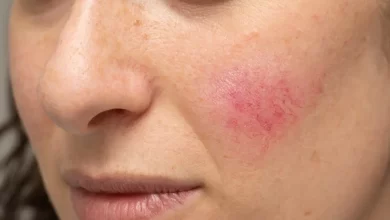
Granuloma Annulare: A Mysterious Skin Condition
One skin condition that often flies under the radar is granuloma annulare. Though not life-threatening, it can be concerning to those who develop it.

What is Granuloma Annulare?
Granuloma annulare is a chronic skin condition characterized by ring-shaped, reddish bumps or lesions. These lesions typically appear on the hands, feet, elbows, or knees but can sometimes affect the entire body.
Though the exact cause remains unknown, possible triggers include:
- Minor skin injuries
- Insect bites
- Infections
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disease
Some evidence suggests that the immune system might play a role in its development, with inflammation localized to the skin.
Symptoms of Granuloma Annulare
- Small, firm, raised bumps arranged in a circle
- Itching (less common)
- Skin discoloration
Most patients experience no pain, but the cosmetic appearance can cause emotional distress.
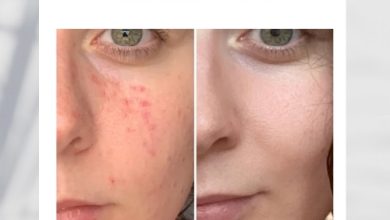
Managing Granuloma Annulare for Better Skin Health
There’s are guaranteed cure for granuloma annulare, several treatment strategies aim to speed healing and improve skin health:
- Topical corticosteroids: Help reduce inflammation.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the lesions can prompt healing.
- Light therapy (PUVA): Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can be beneficial.
- Immunomodulators: In persistent cases, medications that affect the immune response may be prescribed.
Herbal Supplement for Granuloma Annulare relieves eruptions and itching. Patients are also encouraged to practice gentle skincare—avoiding harsh soaps, excessive scrubbing, and irritating chemicals to support skin barrier integrity.
Acne: A Common Obstacle to Skin Health
Acne is arguably the most prevalent skin condition worldwide, affecting millions regardless of age or gender. While it’s most commonly associated with adolescence, many adults continue to battle acne well into their 30s, 40s, and beyond.

What Causes Acne?
Acne develops when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. Contributing factors include:
- Hormonal changes (especially androgens)
- Diet (high-glycemic foods, dairy)
- Stress
- Genetics
- Certain medications
- Poor skincare habits
Bacteria called Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) can worsen inflammation, leading to pustules, nodules, and cystic lesions.
Types of Acne
- Comedonal Acne: Blackheads and whiteheads
- Inflammatory Acne: Papules, pustules
- Cystic Acne: Deep, painful nodules
Each type requires a different management approach, making individualized care critical for optimal skin health.
How to Treat and Prevent Acne
Maintaining skin health while managing acne involves a combination of targeted therapies and lifestyle changes:
Skincare Routine
- Gentle cleansing: Twice daily with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser.
- Exfoliation: Use chemical exfoliants (like salicylic acid) rather than harsh scrubs.
- Moisturizing: Even oily skin needs hydration—opt for oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers.
- Targeted treatments: Topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and azelaic acid.
Prescription Options
- Topical antibiotics: Clindamycin or erythromycin.
- Oral antibiotics: Doxycycline or minocycline for moderate to severe cases.
- Hormonal therapies: Birth control pills or spironolactone.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful option for severe, cystic acne.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet: Emphasize low-glycemic foods, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants.
- Stress management: Mindfulness, yoga, and therapy can help reduce flare-ups.
Consistency is vital. Acne treatments often take several weeks to show results, and abandoning treatment early can sabotage skin health progress.
Sun Protection: Your First Line of Defense for Skin Health
Nothing undermines skin health faster than unprotected sun exposure. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the primary cause of premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and skin cancer.

The Dangers of UV Radiation
- UVA rays penetrate deeply into the skin and cause photoaging (wrinkles, sagging).
- UVB rays are responsible for sunburn and DNA damage leading to skin cancer.
- UVC rays are absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere but can be dangerous with artificial sources.
How Sun Exposure Impacts Skin Health
Chronic sun exposure leads to:
- Breakdown of collagen and elastin
- Hyperpigmentation and age spots
- Formation of wrinkles and leathery skin
- Increased risk of skin cancers like melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma
Effective Sun Protection Strategies
Daily Sunscreen Use
- SPF 30 or higher: Broad-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB rays.
- Reapplication: Every 2 hours when outdoors and after swimming or sweating.
- Ample quantity: Use a nickel-sized dollop for the face alone.
Protective Clothing
- Wide-brimmed hats, UV-blocking sunglasses, and long-sleeve shirts offer added defense.
Seek Shade
- Especially between 10 AM and 4 PM when UV radiation is strongest.
Avoid Tanning Beds
- Artificial UV radiation is equally damaging and heightens the risk of melanoma.
Investing in daily sun protection is one of the most powerful ways to ensure vibrant skin health over the long term.
Anti-aging: Strategies to Maintain Youthful Skin Health
Aging is inevitable, but how we care for our skin can dramatically influence how gracefully we age. Signs of aging—fine lines, wrinkles, sagging skin, and uneven pigmentation—are influenced by intrinsic (genetic) and extrinsic (environmental) factors.

How Aging Affects Skin
As we age:
- Collagen and elastin production decline.
- Hyaluronic acid levels drop, leading to dryness.
- Skin thins and loses firmness.
- Repair mechanisms slow down.
External factors like sun damage, smoking, pollution, and diet accelerate these changes.
Anti-aging Skincare Essentials for Skin Health
Topical Treatments
- Retinoids (Vitamin A derivatives): Boost collagen, improve texture and tone.
- Vitamin C: Powerful antioxidant that brightens skin and neutralizes free radicals.
- Niacinamide: Strengthens the skin barrier and reduces fine lines.
- Peptides: Support collagen production.
Hydration and Moisturization
- Hyaluronic acid serums can plump the skin.
- Rich emollient creams lock in moisture and repair the skin barrier.
Regular Exfoliation
- AHAs (alpha-hydroxy acids) like glycolic acid promote cell turnover and fade hyperpigmentation.
Professional Treatments
- Chemical peels: Improve texture and pigmentation.
- Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production.
- Laser therapies: Target wrinkles, scars, and sunspots.
Lifestyle Factors for Anti-aging and Skin Health
- Balanced diet: Rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins C and E, and lean proteins.
- Adequate sleep: Essential for cellular repair and collagen synthesis.
- Stress management: Chronic stress accelerates aging through cortisol overproduction.
- No smoking: Tobacco toxins destroy collagen and elastin.
- Moderate alcohol intake: Excess alcohol dehydrates the skin and causes inflammation.
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Skin Health
Many natural substances can boost skin health:
- Green tea extract: Rich in polyphenols that protect against UV damage.
- Resveratrol: Antioxidant found in grapes, known for anti-aging properties.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Support a healthy lipid barrier.
- Zinc: Reduces inflammation and promotes wound healing.
- Probiotics: Help maintain a healthy skin microbiome, crucial for acne and eczema prevention.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Daily Routine for Optimal Skin Health
Here’s a simple, universal skincare routine to promote strong, radiant skin:
Morning:
- Gentle cleanser
- Antioxidant serum (Vitamin C)
- Moisturizer
- Sunscreen SPF 30+
Night:
- Cleanser
- Retinoid or targeted treatment
- Hydrating serum (hyaluronic acid)
- Nourishing moisturizer
Weekly:
- Exfoliation (1–2 times)
- Face masks (hydrating or clarifying)
Consistency and patience are crucial for seeing lasting results and preserving skin health.
Conclusion: Your Skin, Your Health
Skin health is deeply intertwined with overall well-being. From managing conditions like granuloma annulare and acne, to practicing vigilant sun protection and adopting anti-aging strategies, the steps we take today lay the foundation for healthy skin tomorrow.
True skin health is not about quick fixes—it’s a lifelong commitment to self-care, protection, and mindful living. By nurturing your skin inside and out, you can enjoy vibrant, resilient, and youthful skin for years to come.