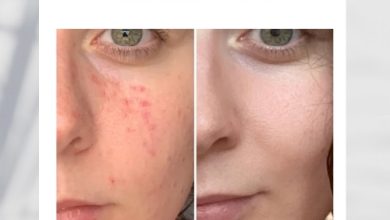
How Strawberry Face Mask for Acne Works

Strawberry Face Mask for Acne
Strawberries are one of the most favorite and commonly consumed fruits in America. Strawberry in years has proven to have a certain kind of acid mostly salicylic acid which makes the skin free of acne. ACNE is one of the most common Skin Problems that affect the daily lives of those who are unluckily experiencing this condition. Strawberry can also help in toning the skin and make the skin pigmentation even lighter and fairer. Furthermore, strawberry has something to do with making the skin elastic and more flexible. Did you know that the acid from the strawberry is being used in different commercial products that beautify the skin? This supports the thought that Strawberry Face Mask for Acne is actually helpful to the skin.
Firstly, strawberries are very low in sugar. One of the great conundrums about fruit is that while they are full of antioxidants and various beneficial phytonutrients like quercetin, they contain lots of natural sugars.Strawberries are a natural source of salicylic acid, one of the most effective acne-fighting agents. Salicylic acid is present as a key ingredient in various acne treatment products.
Strawberries Are Very High in Antioxidants
The most important purpose of antioxidants in preventing acne is preventing your sebum from oxidising. This is the single biggest cause of blocked pores and therefore eating strawberries is a superb way to deprive your acne of the chance to even form in the first place.
Strawberry Mask To Cure Acne Naturally
SAY GOODBYE TO ACNE…! Notorious acne caused by the further accumulation of sebum can be cleared off with the nutrients in this fruit. The acidic nature of strawberries enables it to remove too much oil in the skin.
That’s great for your acne because antioxidants don’t all have the same effects. Numerous antioxidants have their own unique functions; lutein, for instance, is an antioxidant found in eggs that can protect your eyes from blindness.
Strawberry Juice Benefits for Skin
The benefits of strawberry face mask for acne and improve your Skin and Beauty. Using strawberry from anti-aging to removing acne and lightening is the advantage. Strawberries in your beauty routine can be included in various ways. There are strawberry face mask for acne and even strawberry benefits for lips.
Anti-Aging – The ellagic acid and antioxidants save your skin from the UV rays harmful effects and lessen the wrinkling and collagen causing rapidly your skin to age.
Acne – The fruits acidic nature helps to remove additional oil from the skin that is the basic reason for acne.
Skin Lightening – Strawberries have suitable vitamin C known for lightening skin, and to make it smooth and suppler. It can be taken with malic acid, to whiten your teeth. It helps to lighten and as well to hydrate dark lips.
Blackheads – The berry has salicylic acid that is good to exfoliate dead cells and blackheads.
Dark Circles – Strawberries lessen the dark circles and puffiness as they work as astringents.
Some of its benefits are:
- Strawberry face mask for acne is used to slow down the effects of aging.
- Strawberry Mask is usually used to remove the dark circles around your eyes.
- It as well protects you from UV rays.
- Strawberry mask is a pure skin-friendly mixture, due to this property it is used to improve your skin health.
- Strawberry extracts extra oil from your face skin.
- It is also used to heal wounds due to its skin repairing the property.
- Strawberry is also beneficial to soothe mosquito bites.
Why it is good for Skin?
Vitamin C Source:
Vitamin C is perfect for skin as it fights the free radicals that take away from your healthy cells the required oxygen and destroy collagen, thus promoting pronounced lines to show on the skin.
Dietary Fibre:
Strawberries are good to be eaten as dietary fibre and it helps in removing the harmful toxins from our bodies. This is referred to as dietary fibre as it is extremely useful in controlling bowel movement; therefore it prevents constipation that as well relates to causing acne and pimples. The strawberries fibre can help to haveregular toilets and hence help you in having pimple-free skin.
Folic Acid:
The strawberries have folic acid that supports cell regeneration and as well in the production of the new cell in our bodies.
What Should I Do To Strawberry?
- Chop the strawberry and apply it on your face. Rub it lightly for about 20 minutes.
- You can as well have the blended strawberry mixed with sour cream. Apply it on your face as a mask for an hour.
- If you want to apply this as a toner, use the juice of strawberry and pat it on your face with cotton.
- You can as well blend the strawberry with orange peel. Apply it as a mask.
- If there is any fresh leaf with the strawberry, you can use that as well on your face.
Strawberry Mask for Acne
No more oily skin Rich in vitamin C, these fruits can be used to make an excellent strawberry face mask for acne to fight oily skin, as well as nourish and refresh your skin. Strawberries are acidic in nature and this is effective to eliminate the excess sebum on the skin.
- In a bowl, mash a few berries with a fork
- Add 2 Tbs. honey and 1 tsp. lemon juice
- Apply to face for 15 minutes and rinse thoroughly with cool water. You can refrigerate extra strawberry mask in an airtight container for up to a week.
Skin lightening the juice is very effective in lightening blemishes and acne scars. Strawberry juice contains skin lightening extracts as well as ellagic acid which reduce dark spots on skin. Simply apply the juice to the dark spots on your skin using a cotton ball and rinse thoroughly afterward.
Check out the benefit of strawberry face mask for acne, the additional ingredient to this mask visit. Natural Health News
Related Articles:
Why Are Strawberries Good For Skin?
Put Strawberries to Use for a Great Skin
Top 5 Benefits of Strawberries for Skin
Orglow Instant Organic Face Brightening Mask
Clearglow Acne Prone & Problematic Skin Face Mask
Origins Clear Improvement Active Charcoal Mask
Origins Original Skin™ Retexturizing Mask With Rose Clay
Sephora Collection Mud Mask Purifying & Mattifying
Origins Calm To Your Senses™ Mask
Erborianpâte Au Ginseng Black Concentrated Mask
Try This Herbal Mask At Home To Get Rid Of Acne!
8 Homemade Skin Masks for Anti Aging