Glioma Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
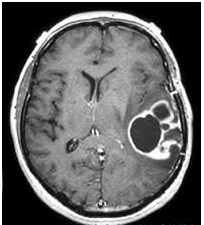
What Is Glioma?
Glioma is a common type of tumor which originates in the brain or spine. Commonly occurring in the brain, Gliomas get their name from glial cells, the site where they arise.
Glial cells are supportive cells surrounding the nerve cells which help the nerve cells to function. There are broadly three types of glial cells and therefore three types of gliomas.
These include:
- Ependymomas
- Such gliomas account for 3% of all brain tumors
- Glial cells involved are called ependymal cells
- Their lack of ability to spread ensures that they can successfully be surgically removed.
- They have a high recurrence rate
- Astrocytomas
- Such gliomas make up 50% of all brain tumors
- Glial cells involved are called astrocytes
- Their ability to spread means that they cannot be cured
- Oligodendrogliomas
- These tumors have a characteristic of spreading to other parts of the body
The symptoms, prognosis, and treatment of a malignant Glioma depend on the person’s age, type of tumor, and the location of the tumor within the brain.
Causes Of Glioma;
The exact cause of gliomas is yet unknown. Hereditary genetic disorders such as neurofibromatoses (type 1 and type 2) and tuberous sclerosis complex are known to predispose their development.
Possible risk factors may include:
- Age.
- People between the ages of 60 and 80 are at a high risk of developing gliomas
- Exposure to radiation.
- Radiation therapy used to treat cancer and radiation exposure caused by atomic bombs can increase the risk
- Family history of Glioma
- Having a family history doubles the chances of developing gliomas
Symptoms Of Glioma:
The signs and symptoms of gliomas may include the following:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Confusion or a decline in brain function
- Memory loss
- Personality changes or irritability
- Difficulty with balance
- Urinary incontinence
- Vision problems, such as blurred vision, double vision or loss of peripheral vision
- Speech difficulties
- Seizures, especially in someone without a history of seizures
Diagnosis Of Gliomas:
Gliomas can be diagnosed via:
- Neurological exam, involving checking of the affected individual’s balance, coordination, vision and hearing ability
- Imaging tests
- MRI
- CT scan
- PET
- Biopsy
Treatment Of Gliomas:
The following treatment options are available:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
By : Natural Health News




