Traumatic Brain Injury Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
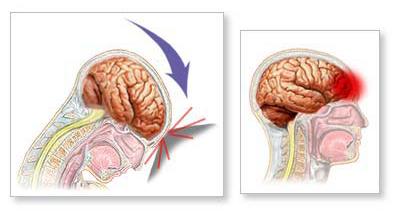
What is Traumatic Brain Injury?
Traumatic Brain Injury is an injury to the brain brought about by a blow or jolt to the head from limit or infiltrating trauma the injury that happens at the moment of impact is known as the primary damage. Primary damage can include a particular lobe of the brain or can include the entire brain. At times the skull might be cracked, however not generally. During the effect of a accident, the brain crashes forward and backward inside the skull bringing on bruising, bleeding and tearing of nerve fibers
Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury
The Causes of Traumatic Brain Injury include
- Falls,
- Motor vehicle and pedestrian-related accidents,
- Collision-related (being struck by or against) events,
- Violent Assaults.
Sport-related injuries and explosive blasts/military combat injuries are other leading causes of Traumatic Brain Injury. Acquiring a brain injury may predispose an individual to additional brain injuries before the symptoms of the first one have resolved completely.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury
Traumatic brain injury can have wide-ranging physical and psychological effects. Some signs or symptoms may appear immediately after the traumatic event, while others may appear days or weeks later.
Mild traumatic brain injury
The signs and symptoms of mild traumatic brain injury may include:
Physical symptoms
- Loss of consciousness for a few seconds to a few minutes
- No loss of consciousness, but a state of being dazed, confused or disoriented
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Difficulty sleeping
- Sleeping more than usual
- Dizziness or loss of balance
Sensory symptoms
- Sensory problems, such as blurred vision, ringing in the ears, a bad taste in the mouth or changes in the ability to smell
- Sensitivity to light or sound
Cognitive or mental symptoms
- Memory or concentration problems
- Mood changes or mood swings
- Feeling depressed or anxious
Moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries
Moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries can include any of the signs and symptoms of mild injury, as well as the following symptoms that may appear within the first hours to days after a head injury:
Physical symptoms
- Loss of consciousness from several minutes to hours
- Persistent headache or headache that worsens
- Repeated vomiting or nausea
- Convulsions or seizures
- Dilation of one or both pupils of the eyes
- Clear fluids draining from the nose or ears
- Inability to awaken from sleep
- Weakness or numbness in fingers and toes
- Loss of coordination
Cognitive or mental symptoms
- Profound confusion
- Agitation, combativeness or other unusual behavior
- Slurred speech
- Coma and other disorders of consciousness
Children’s symptoms
Infants and young children with brain injuries may lack the communication skills to report headaches, sensory problems, confusion and similar symptoms. In a child with traumatic brain injury, you may observe:
- Change in eating or nursing habits
- Persistent crying and inability to be consoled
- Unusual or easy irritability
- Change in ability to pay attention
- Change in sleep habits
- Sad or depressed mood
- Loss of interest in favorite toys or activities
Diagnosis of Traumatic Brain Injury
- Questions about the circumstances of the injury
- Assessment of the person’s level of consciousness and confusion
- Neurological examination to assess memory and thinking, vision, hearing, touch, balance, reflexes and other indicators of brain function
- Depending on the nature of the traumatic brain injury and the severity of symptoms, brain imaging with computed tomography (CT) may be needed to determine if there’s bleeding or swelling in the brain.
Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury
Medications
- Diuretics. .
- Anti-seizure drugs.
- Coma-inducing drugs.
Surgery
- Removing clotted blood (hematomas).
- Repairing skull fractures.
- Opening a window in the skull.
Rehabilitation
- Physiatrist
- Occupational therapist
- Physical therapist,
- Speech and language pathologist
- Neuropsychologist
- Recreational therapist
- Vocational counselor
By : Natural Health News




