Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy ?
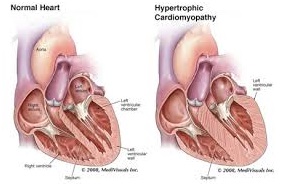
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a primary disease of the muscles of the heart, which is medically known as the myocardium.
It is marked by thickening (hypertrophy) of a portion of the myocardium, which may occur without any apparent cause. This tends to create functional impairment of the cardiac muscle.
A leading cause of sudden cardiac death, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy has high chances of complications in any age group. It may lead to symptoms of disabling cardiac symptoms.
Since hypertrophic cardiomyopathy generally tends to be asymptomatic (pertaining to lack of symptoms) in nature, doctors suggest routinely screening certain populations for the disease.
The thickening of the muscle, which is associated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, is caused by an increase in the size of myocytes, which in turn results in the thickening of the heart muscle.
Approximately, the prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population and often goes undiagnosed due to its lack of symptoms.
Causes Of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy:
Although in most of the cases the cause of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is unknown, it may tend to occur for the following reason:
- Genetic mutation, that results in abnormal thickness of the heart muscle. In such cases hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is inherited
- Development of myofiber disarray, which is marked by abnormal arrangement of myocardium cells
- High blood pressure of aging may lead to development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Symptoms Of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy:
In most of the cases, no symptoms are exhibited by the affected individuals.
However, if symptoms do occur, they include the following:
- Shortness of breath, which may intensify during exercise
- Chest pain, which aggravate during workouts
- Fainting
- palpitation
- Heart murmur
Other than these minor symptoms, the following complications may occur:
- Arrhythmias, which may end up causing s stroke
- Obstructed blood flow.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Mitral valve problems, which may lead to worsening of symptoms
- Heart failure.The thickened heart muscle can eventually become too stiff to effectively fill with blood. As a result, your heart can’t pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs.
- Sudden cardiac death
Diagnosis Of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can be diagnosed via:
- ECG
- Echocardiogram
- Transthoracic echocardiogram
- Transesophageal echocardiogram
- Exercise test
- Cardiac MRI scan
- Cardiac catheterization
- CT scan
- Treadmill stress test
- Genetic testing
Treatment Of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy:
The following treatment options are available:
- Medications
- metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol)
- propranolol (Inderal, Innopran XL)
- atenolol (Tenormin)
- Septal myectomy
- Septal ablation
By : Natural Health News




