Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis (GPA) Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is GPA?
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis or GPA is a serious condition which is known to cause tissue damage.
Formerly referred as Wegener’s granulomatosis, GPA is a systemic disorder which involves both granulomatosis and polyangiitis. A systemic disorder entails inflammation that is present in the entire body.
It is a form of vasculitis, which may affect lungs, respiratory system, kidneys, ears, throat, skin and other organs.
Those whose kidney, brain or gut is not affected in GPA are said to suffer from limited GPA. However, the word ‘limited’ has misleading connotations since it seems to imply that the condition is not serious when in reality the other symptoms may be dangerous enough to prove to be fatal.
A rare disease, GPA can occur in any age. However, it generally occurs to those between the age of 40 and 50.
In recent years, the awareness regarding GPA has grown immensely. This has lead to better diagnoses which may prevent organ failure.
The presence of effective treatment also ensures a relatively normal life for those affected.
Causes Of GPA:
The exact cause of GPA is yet unknown. According to research, its development is linked to infections and other inflammation causing events.
Symptoms Of GPA:
The following signs and symptoms may be exhibited:
- arthritic joint pain
- blood in urine (which may or may not be indicated by a change in urine color)
- cough (with or without the presence of blood)
- fever
- inflammation of the ear with hearing problems
- inflammation of the eye with vision problems
- lack of energy
- loss of appetite
- nasal membrane ulcerations and crusting
- night sweats
- numbness of limbs
- pleuritis (inflammation of the lining of the lung)
- rash and/or skin sores
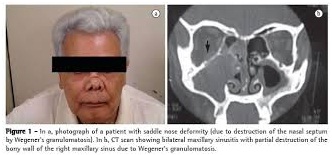
- saddle-nose deformity
- weakness, fatigue
- weight loss
Diagnoses Of GPA:
GPA can be diagnosed via:
- Blood tests, to look for signs of inflammation
- Urine tests, to reveal whether urine contains red blood cells or has too much protein
- Chest imaging, to detect which blood vessels and organs are affected.
- CT scan
- MRI
- X-ray
Treatment Of GPA:
The following treatment options are available:
- Medications
- Corticosteroids to control inflammation
- drugs to suppress immune system
- cyclophosphamide
- azathioprine (Azasan, Imuran)
- Methotrexate (Rheumatrex, Trexall).
- Kidney transplant’
- Plasma exchange
By : Natural Health News




