The Surprising Cooking Oil Behind Sudden Weight Gain
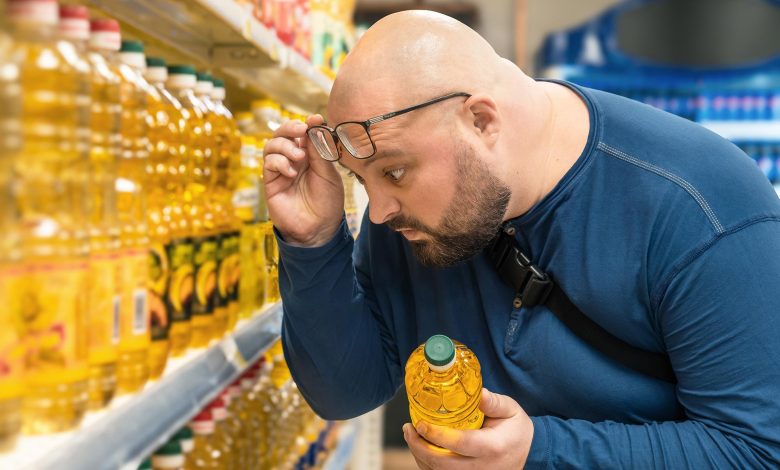

Introduction: Is Your Cooking Oil Secretly Making You Gain Weight?
Most people blame sugar, junk food, or lack of exercise for sudden weight gain — but what if the real culprit is sitting right in your kitchen cabinet?
In recent years, nutritionists and metabolic health experts have increasingly pointed toward a common household ingredient that may be sabotaging your health goals: seed oils, especially soybean oil.
Soybean oil is the most widely used cooking oil in households, restaurants, and processed foods worldwide. It’s cheap, convenient, and marketed as “heart-healthy.” But emerging studies show alarming links between soybean oil consumption and rapid weight gain, inflammation, hormonal disruption, and increased risk of metabolic disorders.
How one of the most common cooking oils can contribute to sudden weight gain, explores the science behind it, and provides healthier alternatives — so you can make informed choices for your long-term well-being.
1. What Is the Cooking Oil Linked to Sudden Weight Gain?
The Answer: Soybean Oil — the Most Widely Consumed Oil in the World
Soybean oil is the surprising ingredient behind unexplained weight gain for millions of people. It’s found in:
- Packaged snacks
- Baked foods
- Fried fast foods
- Margarine
- Salad dressings
- Sauces
- Most restaurant meals
It’s even in foods that don’t taste oily, because manufacturers use it to extend shelf life, enhance texture, and reduce costs. For an average person, up to 70% of daily fat intake may come from seed oils without realizing it.
2. Why Soybean Oil Causes Weight Gain: The Science Explained
2.1 High Omega-6 Fatty Acid Levels Disrupt Metabolism
Soybean oil contains extremely high levels of omega-6 linoleic acid, a fatty acid the body needs only in small amounts. Excessive consumption leads to:
- Inflammation
- Insulin resistance
- Slower fat burning
- Increased fat storage
Chronic inflammation is one of the strongest predictors of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
2.2 It Increases Appetite and Cravings
Research from multiple universities has shown that diets rich in soybean oil can increase hunger signals. Why?
Because omega-6 fats interfere with hormones that control appetite, such as:
- Leptin (satiety hormone)
- Ghrelin (hunger hormone)
When these hormones become imbalanced, people crave more food — especially carbs and sugar — leading to rapid weight gain.
2.3 Soybean Oil Alters Fat Storage in the Body
Seed oils like soybean oil are highly unstable. When heated, they produce oxidized lipids and toxic byproducts that can:
- Damage metabolic tissues
- Promote visceral fat accumulation (dangerous belly fat)
- Increase the risk of fatty liver disease
Animal studies show that soybean oil consumption can lead to higher fat mass even without extra calories.
2.4 It Affects the Gut Microbiome
Your gut bacteria play a major role in weight regulation. Soybean oil has been shown to disrupt the balance of good bacteria in the gut. This leads to:
- Slower metabolism
- Increased fat absorption
- Chronic digestive issues
- Higher inflammation levels
The gut–brain connection means these disturbances can also increase appetite and cravings.
2.5 Soybean Oil May Disrupt Hormones
Some studies suggest that soybean oil — especially genetically modified varieties — can influence hormones linked to:
- Thyroid function
- Estrogen levels
- Metabolic rate
Hormonal imbalance is one of the leading causes of unexplained weight gain, particularly around the stomach and hips.
3. Why Soybean Oil Is Everywhere — And Why You Might Not Notice It
3.1 The Food Industry’s Hidden Ingredient
Soybean oil is cheap to produce and extremely profitable, which is why manufacturers use it extensively. It shows up in ingredient lists under names such as:
- “Vegetable oil”
- “Hydrogenated vegetable oil”
- “Shortening”
- “Lecithin” (derived from soy)
- “Frying oil”
If a label says “vegetable oil,” the majority of the time it is soybean oil.
3.2 Restaurants Use It for Everything
Most restaurants, especially fast-food chains, rely on soybean oil because:
- It’s inexpensive
- It has a neutral taste
- It withstands repeated frying
Even “healthy” restaurant meals often contain it.
3.3 Packaged Foods Depend on It
From granola bars to salad dressings, soybean oil improves texture and shelf stability. This means weight gain triggers can hide in:
- Cereals
- Chips
- Crackers
- Bread
- Microwave meals
- Cookies
- Sauces and dips
Most people don’t connect these everyday items to weight gain, making soybean oil a truly surprising culprit.
4. Signs Your Body Is Reacting to Soybean Oil
You may be consuming too much soybean oil if you experience:
4.1 Sudden weight gain (especially belly fat)
Even with no major changes in diet or exercise.
4.2 Increased hunger and cravings
Especially for sweets and carbs.
4.3 Digestive issues
Such as bloating, indigestion, or constipation.
4.4 Hormonal imbalance
Changes in menstrual patterns, fatigue, or reduced metabolic rate.
4.5 Chronic inflammation
Joint pain, headaches, or skin flare-ups.
4.6 Constant tiredness or brain fog
Seed oils can contribute to mitochondrial dysfunction.
If several of these symptoms appear together, your cooking oil may be playing a significant role.
5. How Soybean Oil Affects Long-Term Health
Sudden weight gain is only the beginning. Extended consumption of soybean oil may contribute to:
5.1 Obesity and metabolic syndrome
Due to inflammation and hormone disruption.
5.2 Type 2 diabetes
Because it increases insulin resistance.
5.3 Fatty liver disease
Soybean oil encourages fat accumulation in the liver.
5.4 Cardiovascular disease
Inflammation and oxidized fats damage arteries.
5.5 Poor brain health
Studies suggest soybean oil may impair genes responsible for brain function.
5.6 Faster aging
Because oxidative stress speeds up cell damage.
These risks make it crucial to reconsider your daily cooking oil choices.
6. The Problem Isn’t Just Soybean Oil — It’s All High-Omega-6 Seed Oils
While soybean oil is the most concerning, several other oils also contribute to weight gain:
- Corn oil
- Sunflower oil
- Canola oil
- Safflower oil
- Cottonseed oil
- Peanut oil
- Grapeseed oil
These oils share similar issues:
- High omega-6 content
- Susceptibility to oxidation
- Refined with chemicals and high heat
- Linked to inflammation and weight gain
Switching away from these oils can dramatically improve health and weight control.
7. Healthier Oils That Support Weight Loss Instead of Blocking It
Not all oils are bad. The key is choosing stable fats that do not oxidize easily and do not disrupt metabolism.
7.1 Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Benefits:
- Protects the heart
- Supports brain function
- Aids weight loss
Best for:
Salads, low-heat cooking.
7.2 Avocado Oil
High smoke point and nutrient-dense.
Benefits:
- Supports metabolism
- Protects cells from damage
- Good for sautéing or roasting
7.3 Coconut Oil
Rich in medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs).
Benefits:
- Boosts energy
- Increases fat burning
- Supports hormones
7.4 Ghee (Clarified Butter)
Highly stable and nutrient-rich.
Benefits:
- Supports digestion
- Nourishes the gut
- Great for high-heat cooking
7.5 Butter (from grass-fed cows)
Benefits:
- Provides butyrate for gut health
- Supports fat-soluble vitamin absorption
Switching to these oils can reverse inflammation, reduce cravings, and support weight loss — often within weeks.
8. How to Remove Soybean Oil From Your Diet
For most people, this is the most challenging part — because soybean oil is everywhere. But with strategic shopping and cooking, it becomes manageable.
8.1 Clean Out Your Kitchen
Check the labels on:
- Cooking oils
- Sauces
- Salad dressings
- Packaged snacks
- Margarine and spreads
Replace anything containing:
- Vegetable oil
- Soybean oil
- Hydrogenated oils
- Lecithin (soy-based)
8.2 Choose Whole Foods Over Processed Ones
The less processed a food is, the less likely it contains hidden seed oils.
8.3 Cook More at Home
This gives you full control over the fats you consume.
8.4 Avoid Deep-Fried Foods
Restaurants rarely use healthy oils for frying.
8.5 Choose Brands That Use Healthy Oils
Look for labels that say:
- “Cooked in olive oil”
- “Made with avocado oil”
- “No seed oils”
Seed-oil-free brands are gaining popularity.
9. What Happens When You Stop Consuming Soybean Oil?
People often notice improvements quickly. Within 1–4 weeks of avoiding soybean oil, many report:
9.1 Reduced bloating
Inflammation begins to subside.
9.2 Fewer cravings
Hormones start balancing naturally.
9.3 More stable energy
Healthy fats improve mitochondrial function.
9.4 Faster metabolism
Your body burns fat more efficiently.
9.5 Noticeable weight loss
Especially around the midsection.
9.6 Improved skin health
Reduced acne and inflammation.
9.7 Better mental clarity
Seed oils contribute to fogginess.
Over months, risks of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease also decrease.
Conclusion: Switching Your Cooking Oil Could Change Everything
Sudden weight gain can be confusing and frustrating — especially when your diet and lifestyle seem unchanged. But the surprising truth is that one of the most common cooking oils in the world may be quietly undermining your health.
Soybean oil, a major component of the modern diet, contributes to:
- Increased fat storage
- Hormonal imbalance
- Chronic inflammation
- Persistent hunger
- Gut disruption
By reducing or eliminating this oil from your diet and switching to healthier alternatives, you can dramatically improve your metabolism, energy levels, and overall well-being.