Pulmonary Fibrosis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment
What Is Pulmonary Fibrosis ?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a respiratory disease which is characterized by formation of scars in the lung tissues. This may lead to serious breathing problems.
Such scarring may arise due to a number of factors. It ranges from environmental factors to infections.
Accumulation of excess fibrous connective tissue may lead to thickening of the walls which then reduces the amount of oxygen supplied. This in turn may lead to shortness of breath.
While the cause of the disease may be successfully determined in some of the cases, the same cannot be said about all of the affected individual. If the cause cannot be determined, the condition is referred to as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
While pulmonary fibrosis is incurable, treatment options are available to manage the issue. Depending on the severity of the condition, lung transplant may be recommended by the doctors.
Causes Of Pulmonary Fibrosis:
If pulmonary fibrosis occurs without any known cause, it is dubbed to be idiopathic in nature.
Pulmonary fibrosis may be a secondary effect of other diseases. Most of these are classified as interstitial lung diseases. Examples include:
- autoimmune disorders
- viral infections
- Bacterial infection
- tuberculosis
Diseases and conditions that may cause pulmonary fibrosis as a secondary effect include:
- Inhalation of environmental and occupational pollutants
- metals in asbestosis
- silicosis
- exposure to certain gases
- Cigarette smoking
- Some typical connective tissue diseases
- rheumatoid arthritis
- SLE
- scleroderma
- sarcoidosis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
- Infections
- Certain medications,
- amiodarone
- bleomycin (pingyangmycin)
- busulfan
- methotrexate
- nitrofurantoin
- Radiation therapy to the chest
Symptoms Of Pulmonary Fibrosis:
Signs and symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath, particularly with exertion
- Chronic dry, hacking coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest discomfort including chest pain
- Loss of appetite
- rapid weight loss
Diagnosis Of Pulmonary Fibrosis:
The following tests and exams may be conducted to diagnose pulmonary fibrosis:
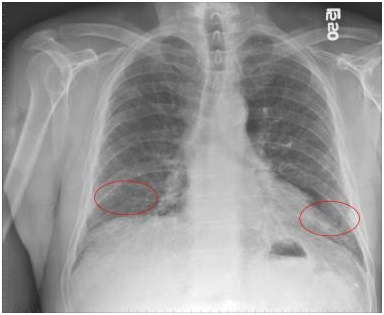
- Imaging tests
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
- Echocardiogram
- Lung function test
- Pulmonary function test
- Oximetry
- Exercise stress test
- Biopsy
- Bronchoscopy
- Surgical biopsy
- Broncho alveolar lavage
Treatment Of Pulmonary Fibrosis:
The following treatment options are available:
- Medications
- Corticosteroid
- Oxygen therapy
- Reduces blood pressure
- Improves sleeping pattern
- Makes breathing easier and less painful
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Physical exercise
- Breathing techniques
- Nutritional counselling
- Support
- Surgery
- Lung transplant
By : Natural Health News