Cluster Headache Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Are Cluster Headaches?
Cluster headache (CH) is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, severe headaches on one side of the head, typically around the eye.
Cluster headache belongs to a group of primary headache disorders, classified as the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias or (TACs)
Bouts of frequent attacks, known as cluster periods, may last from weeks to months, usually followed by remission periods when the headache attacks stop completely.
They usually start at the age of 30 and are more common in men than women.
Causes Of Cluster Headache:
The exact cause of cluster headaches are yet unknown.
However, the following factors may play a role:
- Genetics
- Cluster headache may, but rarely, run in some families in anautosomal dominant inheritance pattern.
- People with afirst degree relative with the condition are more likely to develop it themselves,
- Tobacco smoking
- Dysfunction of the hypothalamus
- Alcohol use
Symptoms Of Cluster Headache:
Common signs and symptoms may include the following:
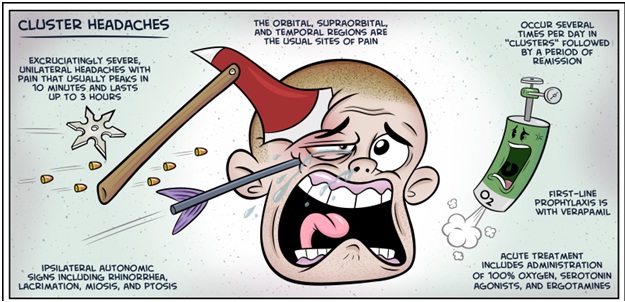
- Excruciating pain, generally located in or around one eye, but may radiate to other areas of the face, head, neck and shoulders
- One-sided pain
- Restlessness
- Excessive tearing
- Redness in the eye on the affected side
- Stuffy or runny nasal passage in the nostril on the affected side of the face
- Sweaty, pale skin (pallor) on the face
- Swelling around the eye on the affected side of the face
- Drooping eyelid
Diagnosis Of Cluster Headache:
After taking a medical history, the doctor may conduct the following tests and exams in order to diagnose cluster headaches:
- Neurological examination
- Imaging tests
- CT scans
- MRI
Treatment Of Cluster Headache:
There is no cure for cluster headaches.
Treatments are available which aim to reduce the severity of pain and to shorten the headache period.
Treatment options include:
- Acute treatments
- Oxygen
Briefly inhaling 100 percent oxygen through a mask at a minimum rate of at least 12 liters a minute provides dramatic relief for most who use it.
- Triptans
- Octreotide
- Local anesthetics
- Dihydroergotamine
- Preventive treatments
- Calcium channel blockers
- Corticosteroids
- Lithium carbonate
- Nerve block
- Ergots
- Melatonin
- Surgery
By : Natural Health News