Group B Streptococcus Infection Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Group B Streptococcus Infection?
Group B Streptococcus infection is the infection which is caused by the bacteria known as “Streptococous agalactiae”.
The bacterium is known to cause extreme illness and may at times prove to be fatal. The associated mortality rates are significantly higher in newborns, elderly and people with weakened immune system.
Moreover, it is likely to affect those with chronic medical conditions. These may include diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
A gram-positive strep bacterium, Streptococcus agalactiae is generally found in the human body and does not cause any symptoms in healthy non pregnant individuals.
Group B strep infection is known to cause a variety of complications which range from meningitis to sepsis.
The incidence of Group B strep infection in adults increases with age, with the highest rate in adults 65 years of age
Although the incidence of neonatal group B strep infection has been decreasing, the incidence of group B strep infection in non pregnant adults has been increasing.
Causes Of Group B Strep Infection:
Group B strep bacteria are naturally found in healthy people. Such people may or may not exhibit any symptoms.
Neither is such bacteria sexually transmitted, nor transmitted via contaminated food or water.
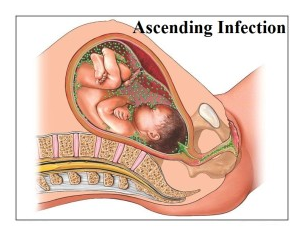
Group B strep can spread to a baby during a vaginal delivery if the baby is exposed to fluids containing group B strep.
Moreover, some individuals with chronic health conditions can develop a more serious infection from group B strep. However, the reason this occurs in some people but not others isn’t known.
The major cause of strep infection in unborn babies is the transmission of the bacteria from the mother to the fetus.
Maternal risk factors that increase the chance of transmitting group B strep to the newborn leading to early onset disease:
- Labor or membrane rupture before 37 weeks gestation
- Membrane rupture more than 18 hours before delivery
- Urinary tract infection with GBS during pregnancy
- Previous baby with GBS infection
- Fever during labor
- Positive culture for GBS colonization at 35-37 weeks
Other risk factors in infants may include:
- The baby is born earlier than 37 weeks
- The mother’s water breaks 18 hours or more before delivery
- The mother has chorioamnionitis
- Bacteriuria during pregnancy
- The mother’s temperature is high during labor
- The mother previously delivered an infant with group B strep disease
Symptoms Of Group B Strep Infection:
The following symptoms are exhibited:
- Fever
- Difficulty feeding
- Lethargy
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever
- Difficulty feeding
- Lethargy
- Irritability
Diagnosis Of Group B Strep Infection:
Group B infection can be diagnosed via:
- Strep screening
- Taking swab samples from vagina or rectum
- Blood test for evaluation
Treatment Of Group B Strep:
The following treatments are available:
- Intravenous antibiotics for infants
- penicillin or cephalexin for adults
By : Natural Health News