Bunions Causes, Symptoms, Diangosis and Treatment
What Is Bunions?
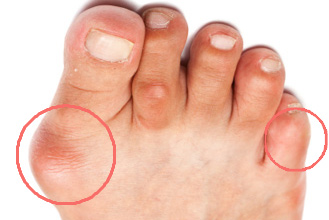
A bunion is a deformity of the joint connecting the big toe to the foot and is known as a hallux abducto valgus among medical professionals.
It is characterized by medial deviation of the first metatarsal bone and lateral deviation of the hallux (big toe), often erroneously described as an enlargement of bone or tissue around the joint at the bottom of the big toe (known as the metatarsophalangeal joint).
Wearing tight, narrow shoes might cause bunions or might make them worse. Bunions can also develop as a result of an inherited structural defect, stress on the foot or a medical condition, such as arthritis.
Smaller bunions (bunionettes) also can develop on the joint of the little toes.
Possible complications of bunions include:
- Bursitis.
It occurs when the small fluid-filled pads (bursae) that cushion bones, tendons and muscles near the joints become inflamed. - Hammertoe.
An abnormal bend that occurs in the middle joint of a toe, usually the toe next to the big toe, can cause pain and pressure. - Metatarsalgia.
It causes pain and inflammation in the ball of one’s foot.
Causes Of Bunions:
The exact cause of bunions is yet unknown.
However, possible causes of bunions may include:
- genetics (family history)
- arthritis
- other conditions and syndromes
cerebral palsy
Marfan syndrome - poorly fitting shoes
- Foot injuries
- Congenital deformities
Women are especially prone to developing bunions. Years of wearing tight, poorly fitting shoes, especially high-heeled, pointed shoes, can bring on bunions. Such shoes gradually push the foot bones into an unnatural shape.
Symptoms Of Bunions:
The signs and symptoms of a bunion include:
- A bulging bump on the outside of the base of the big toe
- Swelling, redness or soreness around the big toe joint
- Thickening of the skin at the base of the big toe
- Corns or calluses — these often develop where the first and second toes overlap
- Persistent or intermittent pain
- Restricted movement of the big toe
Diagnosis Of Bunions:
Bunions can be diagnosed via:
- A physical examination, to determine if range of motion is limited
- X-ray, to identify the cause and severity of the bunion
Treatment Of Bunions:
The following treatment options are available:
- Conservative treatment
Changing shoes.
Padding and taping or splinting, to reduce stress on the bunion and alleviate pain.
Medications.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol, others)
ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others)
naproxen (Aleve)
Shoe inserts, to distribute pressure evenly.
Applying ice, which help relieve soreness and inflammation - Surgical options
Removing the swollen tissue from around the big toe joint
Straightening the big toe by removing part of the bone
Realigning the long bone between the back part of the foot and the big toe, to straighten out the abnormal angle in the big toe joint
Joining the bones of the affected joint permanently
By : Natural Health News